It means when the business generates revenue beyond the break-even point, it starts earning profits. The management can set a specific amount as target profit above that break-even point. Target profit analysis is about finding out the estimated business activities to perform to earn a target profit during a certain period of time. Among these activities, management is especially interested to find out the sales volume required to generate a target profit. Target profit is the expected amount of profit that the managers of a business expect to achieve by the end of a designated accounting period.
Steps To Follow
The second step is to draw the graph with the cumulative sales showing on the x-axis and the profit on the y-axis. The methods discussed above are useful for a single-product facility or a manufacturing facility with a limited number of products. However, in many cases, which transactions affect retained earnings there are several similar products manufactured in the same facility. If it is set to zero in the above equation, it will give the break-even point in terms of sales. However, many businesses fail to achieve it through this approach as they cannot control budgets.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Profit Percentage
Let’s say a business has annual fixed costs of £65,000, variable costs per unit of £10 and a selling price per unit of £30. Knowing what target profit is sets the stage for understanding its role in business. Target profit acts like a compass for companies, guiding them towards financial success. It’s not just about making money; it’s about knowing how much money needs to be made to cover costs and achieve growth. Unit variable costs and production volume will remain constant and in proportion as the production level changes.
Optimizing Financial Performance Through Sales Mix Variance Analysis
And with real-life examples backing up our advice, you’re sure to grasp the concepts more readily. You might find yourself asking, “How can I predict whether my sales will hit that sweet spot where profits rise? ” This common plight can lead to missed opportunities and growth stagnation if not tackled head-on.

By understanding these cost structures, companies can better manage their resources and optimize their operations. As an illustration, suppose a start up manufacturing business wants to target a profit of 15,000 in its financial projections. Additionally its product sells for 15.00 and costs 6.75 to produce, and it has fixed costs of 60,000. The number of units it needs to sell to reach its profit target is as follows. In addition to its strategic applications, sensitivity analysis also enhances internal decision-making processes.
The total fixed costs apportioning will change as the volume of production changes. Understanding the impact of sales mix on profit is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their product portfolio and maximize profitability. The sales mix refers to the proportion of different products or services that a company sells. Since each product typically has a different profit margin, the overall profitability can be significantly influenced by changes in the sales mix. For instance, a company that sells both high-margin and low-margin products will see its profit margins fluctuate based on the proportion of each sold. The management can use the graphical method to calculate the break-even sales points as well as target profits for each product.
- These steps will help keep financial performance on track and support business growth.
- Draw a line that represents the profit of P1 (the highest-ranked C/S product) scaled to the graph on the y-axis.
- The first step is to determine the profitability of each product and rank them accordingly.
- It helps management set profit targets to increase operational efficiency.
However, it also offers some limitations in the form of variance in results, employee demotivation, and unrealistic approaches from the management. Target profit is an integral part of the cost-volume-profit or the CVP analysis. It helps management set profit targets to increase operational efficiency. Without setting time limits the practice of the target profit approach would be futile. For instance, a business can set a dollar amount to achieve through increased sales. Profit percentage is more than just a financial metric it’s a powerful tool that can drive strategic decision-making and business growth.
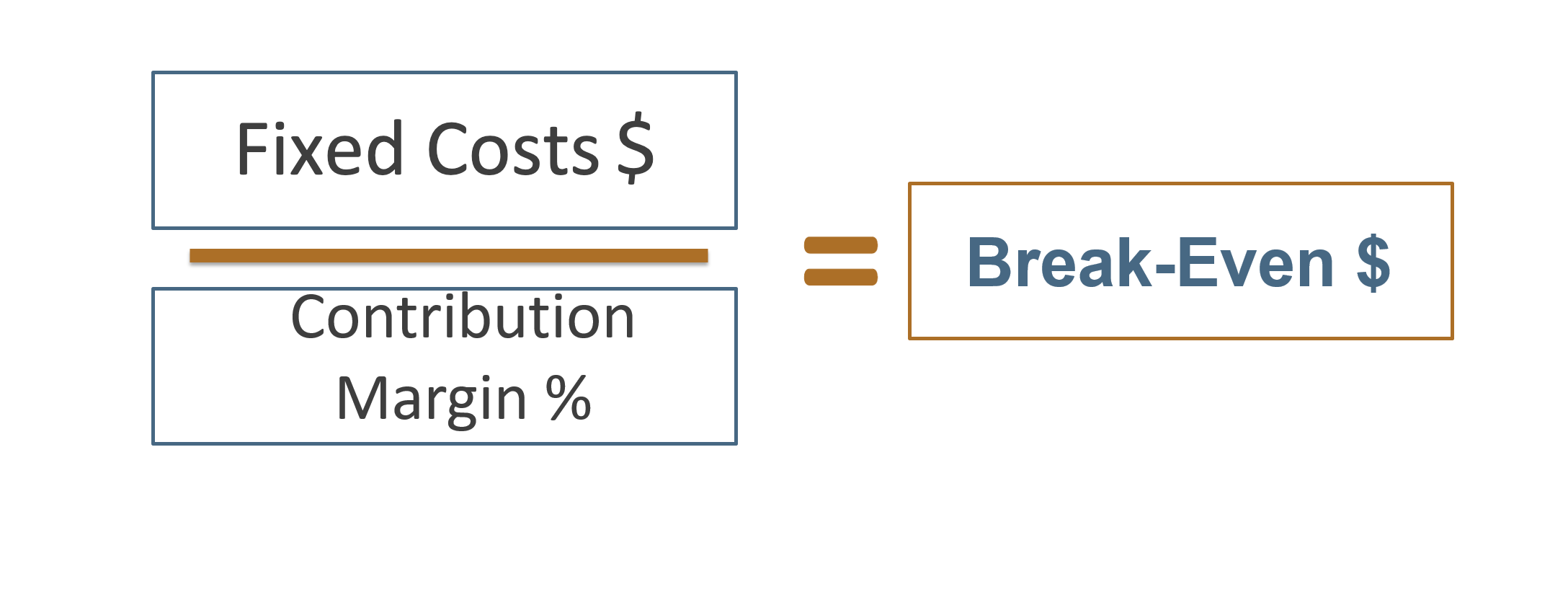
Again, setting the target profit to zero will give the sales break-even point. In above CVP chart, red dot represents break-even sales and blue dot represents target sales. We can observe that the corporation breaks even at a sales volume of $1,120,000 and target sales for the next year are $1,680,000 which are $560,000 higher than the break-even sales. Notice that to get target profit formulas or equations, we have just included the target profit to break-even point formulas.
Here are a few advantages of using the target profit approach as compared to the arbitrary budgeting method. The first step is to determine the profitability of each product and rank them accordingly. The graphical method of the profit-volume analysis assumes that the company must sell its most profitable product first. The above equation can be used with a little variation of using the C/S ratio instead of the contribution margin. The management can then add the desired profit that comes through excess of the break-even point sales. Since budgets come with inevitable variances, an alternative method is desired.

