These expenses stay the same regardless of the level of production, so per-item costs are reduced if the business makes more widgets. Nonetheless, additional production always generates additional manufacturing costs. A lower per-item fixed cost motivates many businesses to continue expanding production up to its total capacity. This allows the business to achieve a higher profit margin after considering all variable costs. As the rate of production increases, the company’s revenue increases while its fixed costs remain steady. Therefore, the per-item cost of manufacturing falls and the business becomes more profitable.
What are Nonmanufacturing Overhead Costs?
Clockify is a time tracker and timesheet app that lets you track work hours across projects. Pricing services feels like a high-stakes gamble for every business owner. Learn about some easy-to-apply ways for monthly expense tracking, with methods. A project cost overrun happens when the project costs exceed the budget estimate.
Keep Your Business Afloat With These Budgeting Methods
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com. This account is a non-operating or “other” expense for the cost of borrowed money or other credit.
Direct Labor
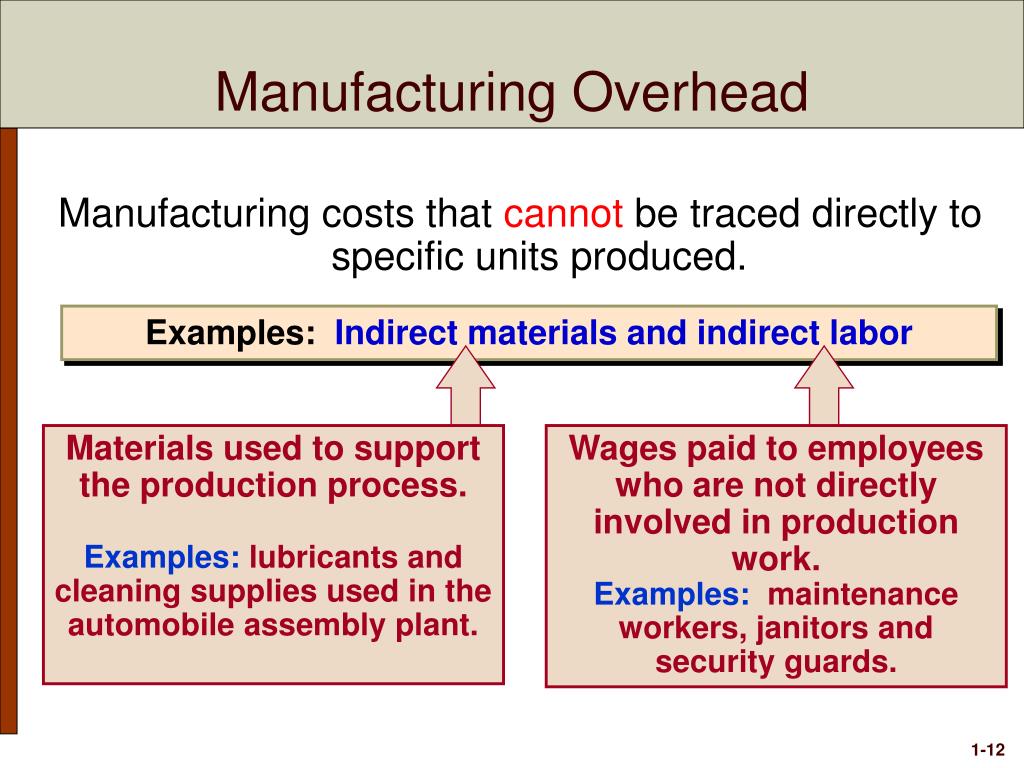
Manufacturing costs, also called product costs, are the expenses a company incurs in the process of manufacturing products. Costs that fluctuate based on the level of production or sales, such as raw materials and direct labor. Examples of general and administrative costs include salaries and bonuses of top executives and the costs of administrative departments, including personnel, accounting, legal, and information technology.
General and Administrative Costs
Entities may manufacture several types of products and the sum total of all the costs involved in producing those products is termed as manufacturing cost. The team calculated that 370 million tons of these nine materials were manufactured in the United States in 2018, resulting in 427 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions. This resulted in $79 billion of climate costs that are not included in the market prices of these materials. They gathered data on the amounts of these materials produced in the United States, the energy used to make them and the greenhouse gas emissions from the manufacturing process. They assessed the climate costs of emissions using the Environmental Protection Agency’s Social Cost of Carbon standard. This is an estimate of the costs of carbon dioxide emissions, such as preventing, mitigating and recovering from climate-related natural disasters.
It basically includes a fixed cost potion plus additional variable costs. An example would be electricity expense that consists of a fixed amount plus variable charges based on usage. This is important because while climate costs of energy can be reduced by switching to renewable sources, process costs are fixed unless we can develop new processes or substitute materials. For example, manufacturing aluminum generates quite a lot of carbon dioxide per weight of product, while making the same amount of brick generates much less. But the tonnage of bricks produced every year is far higher than that of aluminum, so making bricks contributes more to climate costs overall than making aluminum. Table 2.3.1 provides several examples of manufacturing costs at Custom Furniture Company by category.
- The second part of the necessary entry will be a credit to a liability account.
- By looking at the historic data on employee timesheets and purchasing costs, the firm was able to understand the areas that were increasing the total manufacturing costs.
- By calculating manufacturing costs, companies can clearly understand the true cost of making a product.
- Now, add the value of existing inventory to the cost of purchasing new inventory to calculate the cost of direct materials.
- This account is a non-operating or “other” expense for the cost of borrowed money or other credit.
For a manufacturer these are expenses outside of the manufacturing function. Instead these expenses are reported on the income statement student loan interest deduction of the period in which they occur. Nonmanufacturing, also known as “period” costs, consists of selling and administrative expenses.
They are impacted by different factors and thus their appropriate categorization is important. Manufacturing cost overruns indicate production inefficiency whereas non-manufacturing cost overruns indicate inefficiency in other areas of operations. Each of them requires a different set of cost control measures, making appropriate cost categorization even more essential. Note “Business in Action 2.3.2” provides examples of nonmanufacturing costs at PepsiCo, Inc. Note 1.48 “Business in Action 1.6” provides examples of nonmanufacturing costs at PepsiCo, Inc. The two broad categories of costs are manufacturing costs and nonmanufacturing costs.
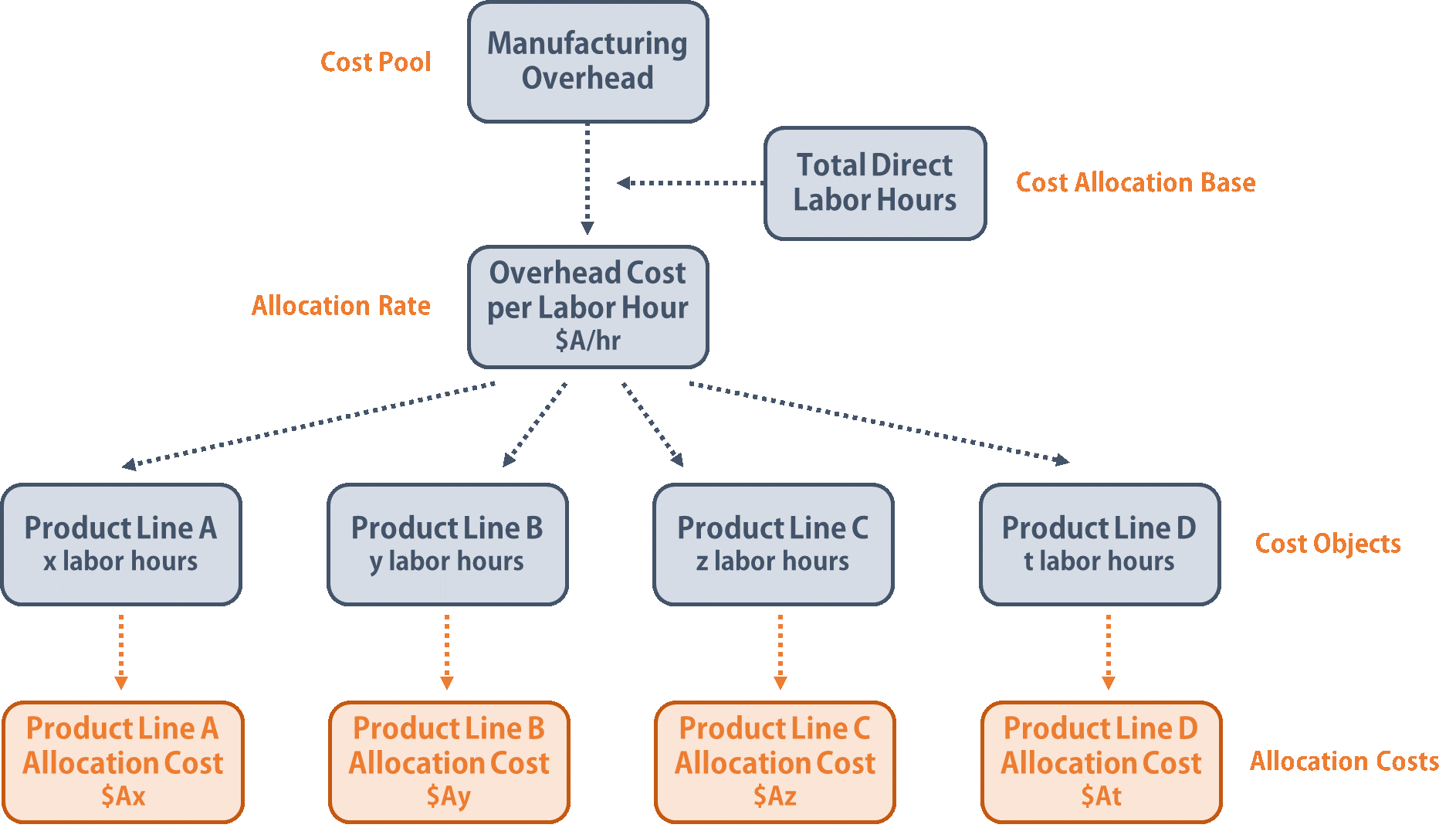
However, for management objectives, managers frequently require the assignment of nonmanufacturing costs to goods. This is especially true for specific product-related commissions and promotions. Once you identify the indirect costs, get detailed expense data for each of these overhead cost categories for a specific period, such as a month or a year. You can track expenses by looking at your invoices, receipts, and records of all expenditures related to manufacturing overhead. These indirect costs, also called factory or manufacturing overheads, include costs related to property tax, insurance, maintenance, and other indirect operations that support the production process.
Controllable costs – refer to costs that can be influenced or controlled by the manager. Segment managers should be evaluated based on costs that they can control. “When considering new technologies, such as biomass-based plastics, if we can account for the benefit of carbon storage in the material, we can make them more cost-effective in the market,” Van Roijen said. Kavitha Simha is a productivity author and researcher, passionate about finding smarter ways to manage time. Combining her knowledge of multiple disciplines, she seeks to help others optimize their work-life balance, which she believes is the key to minimizing stress. Effectively managing expenses in manufacturing isn’t just an option — it’s a necessity.

